Javascript Promise Practical examples

Example:
An asynchronous request to a web service that returns data:
const myPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Instantiating the request
const request = new XMLHttpRequest();
// Opening a request
request.open('GET', 'https://divercity-test.herokuapp.com/jobs');
// check the status in onload method
request.onload = () => {
if (request.status === 200) {
resolve(request.response); // Set resolve callback
} else {
reject(Error(request.statusText)); // Set reject callback
}
};
// onError method
request.onError = () => {
reject(Error('Error fetching data.')); // Set reject callback
}
// Sending the request
request.send();
})
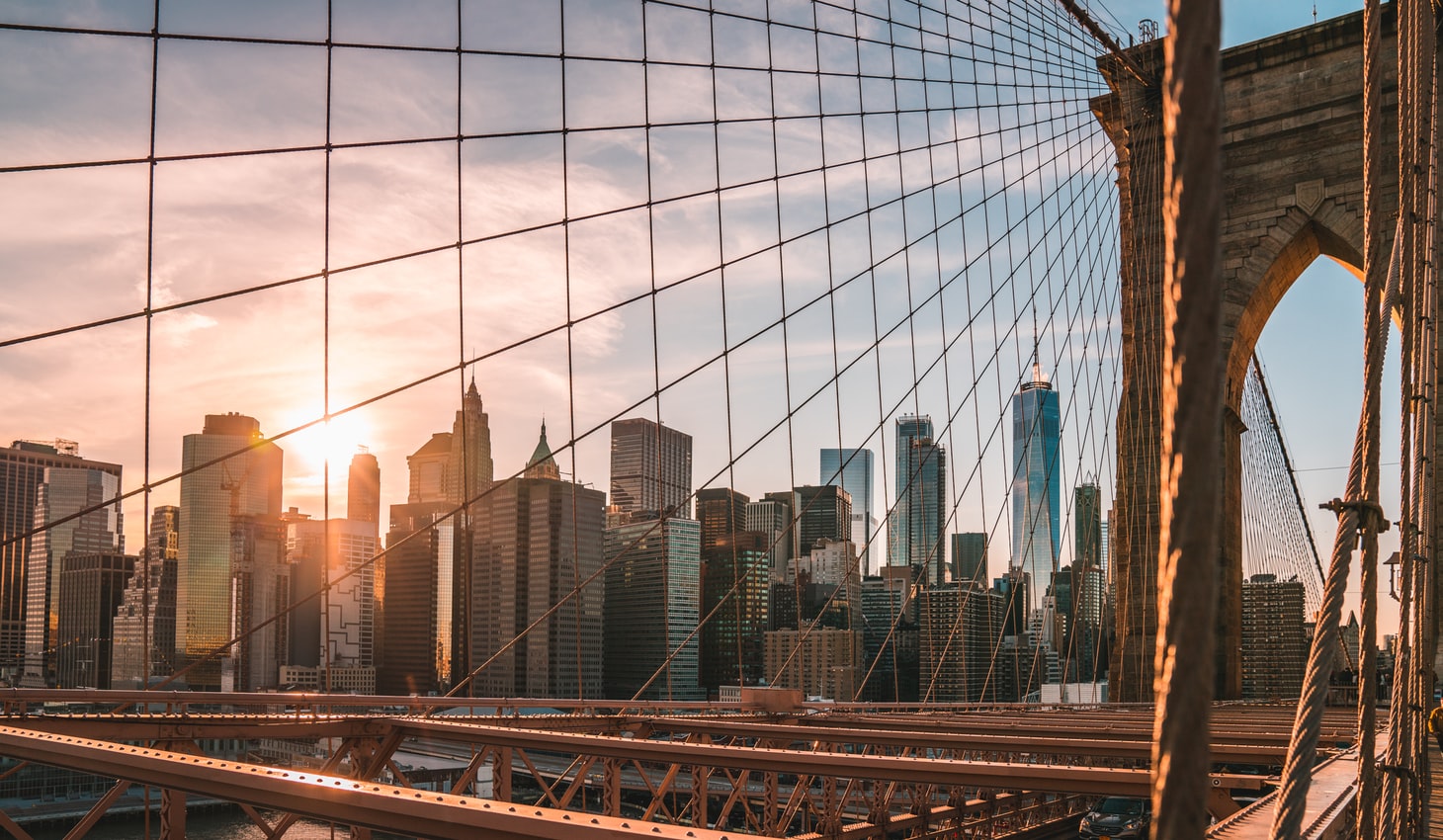
// Accessing to my promise results
myPromise
.then((data) => {
// JSON.parse() to convert text into a JavaScript object
console.log('data --->', JSON.parse(data));
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log('Promise Rejected --->', error.message);
});Result:
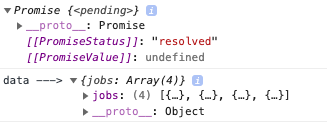
Example:
We can fetch data using the Javascript method called “fetch“, this method is also a Promise, check the next example:
// API endpoint path
const url = 'https://divercity-test.herokuapp.com/jobs';
fetch(url)
.then(data => data.json()) // parsing the body text as JSON
.then(response => {
console.log('response -->', response)
});Result:
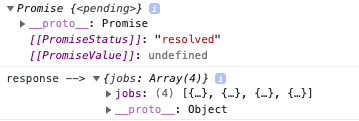
Example:
We can chain multiple Promises, but remember that this would be “recursion” operations
function division(numberA, numberB) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (numberB === 0) {
reject(Error ('cannot be divided by zero'));
}
return resolve(numberA / numberB);
})
}
let myPromise = division(64, 2);
myPromise
.then((result) => {
console.log('result --->', result);
return division(result, 2);
})
.then((res) => {
console.log('res --->', res);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
});Result:
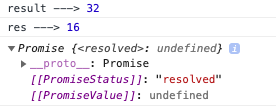
Example
We can have a setTimeout (is Asynchronous operation) inside of our Promise, like this:
function later(delay) {
// Promise
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { // Promise is Asynchronous operation
setTimeout(() => { // setTimeout is also Asynchronous operation
const enter = false;
if (enter) {
resolve('hola')
} else {
reject(Error('was rejected'));
}
}, delay); // until 3 seconds - Fulfilled state of Promise
})
}
later(3000)
.then((result) => {
console.log('result ->', result);
})
.catch((error) => {
console.log(error);
});Result:
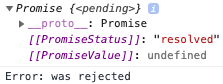
The last example Promise state is Fulfilled and status is resolved.
By Cristina Rojas.




