Programming interview questions

Hi, in this post you will find a list of some programming interview questions that you can use to evaluate the candidate technical skills.
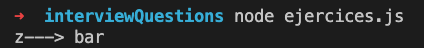
1.- What is the value of z after the following code runs?
let x = { 'foo': 'bar' };
let y = {'baz': x};
let z = y['baz']['foo'];
console.log('z--->', z);Answer:
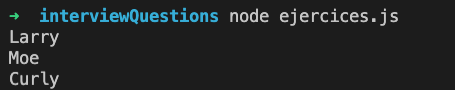
2.- What’s the expected output of the following JavaScript code?
function foo() {
function bar() {
setTimeout(
() => console.log('Curly'), // 3 execution
1000);
}
console.log('Larry'); // 1 execution
return bar;
}
let x = foo();
x();
console.log('Moe'); // 2 executionAnswer:
3.-What is the value of g after the following code block runs?
function f(x) { // (3)
x *= 2; // 3 x 2 = 6 ---> x = 6 now
return function(y) { // (4)
y *= x; // 4 x 6 = 24 ---> y = 24 now
return function(z) { // (5)
return z * y; // 5 x 24 = 120 ---> z = 120 now, the finall return is 120
}
}
}
let g = f(3)(4)(5);
console.log(g); // 120Answer:

4.- Fill in the missing code
Get the cumulative sum of a list
Example: acumulative_sum([1,2,3,4,5]); the result will be => [ 1, 3, 6, 10, 15 ]
function acumulative_sum(list) {
let output = [];
for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
output.push(list[i]);
} else {
// your code here
}
}
return output;
}
let result = acumulative_sum([1,2,3,4,5]);
console.log('result--->', result);Answer:
function acumulative_sum(list) {
let output = [];
for (let i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
output.push(list[i]);
} else {
output.push(list[i] + output[i-1]);
}
}
return output;
}
let result = acumulative_sum([1,2,3,4,5]);
console.log('result--->', result);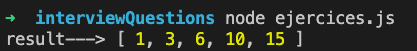
5.- Fill in the missing code
function strToFloat(str) {
// Your code here
}
let result = strToFloat('.5');
console.log('result --->', result);
console.log('result type --->', typeof result);Answer:
function strToFloat(str) {
return parseFloat(str); // parses a string and returns a floating point number.
}
let result = strToFloat('.5');
console.log('result --->', result);
console.log('result type --->', typeof result);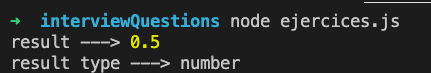
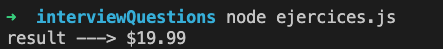
6.- What is the value of the variable eventPrice after the following code runs?
let event = {
name: "Hot Dog and Burger Sunday",
financials: {
baseCost: "$19.99",
discountAvailable: false,
maxCost: "$29.99"
},
subscribers: [
]
};
let eventPrice;
// Destructuring that get baseCost property also rename that property by price
const assignEvent = ({ financials: { baseCost: price }}) => eventPrice = price; // assign price value to the variable eventPrice.
let result = assignEvent(event); // Assigning an object to the function
console.log('result --->', result);Answer:
7.- In what order does f receive its arguments?
f("foo");
setTimeout(function() { f("bar"); }, 0);
f("baz");Answer:
foo, baz, bar -> because this reason.
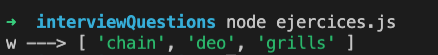
8.- Which of the las four variables contains the array [“chain”, “deo”, “grills”] ?
const getItemsOrderByCustomer = customer => (...orders) => {
return orders.filter(order => order.customerId === customer.id)
.map(order => order.items)
.reduce((acc, cur) => [...acc, ...cur], []);
}
let customer = {
name: "fiddy",
id: 5
};
const order1 = { id: 1, customerId: 1, items: ["belt"]};
const order2 = { id: 2, customerId: 5, items: ["chain", "deo"]};
const order3 = { id: 3, customerId: 5, items: ["grills"]};
const order4 = { id: 4, customerId: 2, items: ["pants"]};
const w = getItemsOrderByCustomer(customer)(order1, order2, order3, order4);
const x = getItemsOrderByCustomer(customer)([order1, order2, order3, order4]);
const y = getItemsOrderByCustomer(customer, order1, order2, order3, order4);
const z = getItemsOrderByCustomer(customer)(order1, order2, order4);Answer:
The w const is the answer.
9.- What does the following code do?
function myStr(str) {
return str.split('dog').join('cat');
}
console.log(myStr('cristina hola dog xxxx dog yyy'));Answer:

By Cristina Rojas.




