GraphQL course implementing a resolver function

Now is time to provide the implementation that specifies exactly how the server return the “greeting value“.
Note: last GraphQL chapter was GraphQL course defining a schema
We are going to do that by creating an object called “resolvers” the resolver need to match to the type definition
const resolvers = {}The the object need a property called Query & Query will be a nested object because it represent a type
const resolvers = {
Query: {}
}And Query object have a property called “greeting” just like the field that we declared in the type definition and this will be a function that will return the value our of greeting.
const resolvers = {
Query: {
greeting: () => 'Hello world!'
}
}So, that function will be called by the GraphQL engine every-time that the client sends the greeting query or in other words this function will be called to resolve the value of the “greeting field” this is why is called a resolver function and also why we call the hole of object as “resolvers“.
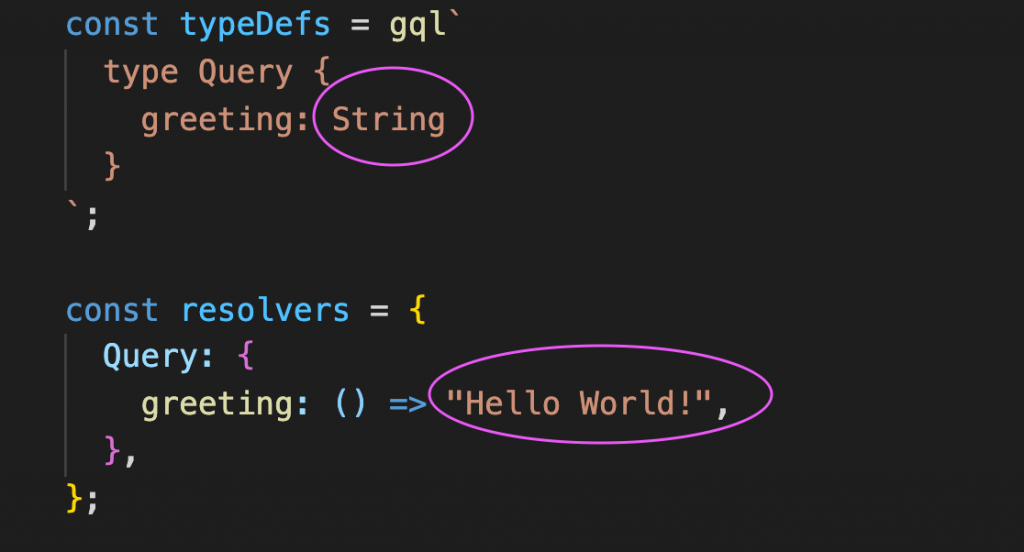
So, resolve have Query and greeting as same as type definition:

If you see the greeting type definition is string type so the resolver function is returning an string:
The next step is create our server, so to do that we need to import the ApolloServer class from “apollo-server”:
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require("apollo-server");ApolloServer class is needed because we need a new instance from that Class like this:
const server = new ApolloServer({});Then the ApolloServer constructor take an object where we can pass configuration properties:
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });Finally we need to start our server calling .listen() method and this method also take a configuration object as parameters:
server
.listen({ port: 9000 })Since .listen() method return a promise over <ServerInfo> we can call .then() that take ServerInfo as argument and log a message to the console.
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
server
.listen({ port: 9000 })
.then((serverInfo) => console.log(`Server running at ${serverInfo.url}`));
Now is time to run our GraphQl sever by running “node server.js” in the terminal:

All server.js code:
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require("apollo-server");
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
greeting: String
}
`;
const resolvers = {
Query: {
greeting: () => "Hello World!",
},
};
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
server
.listen({ port: 9000 })
.then((serverInfo) => console.log(`Server running at ${serverInfo.url}`));
By Cristina Rojas.




